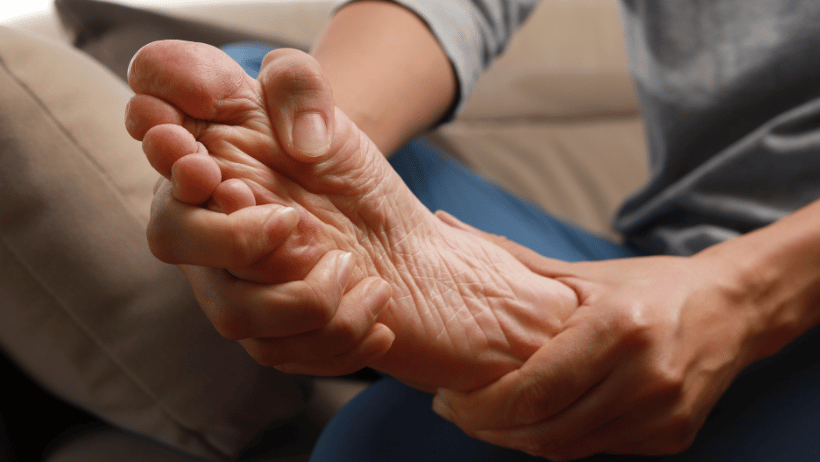
Gout is a type of arthritis that commonly affects the elderly population. It is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. These crystals can lead to inflammation, pain, and swelling.
This condition can greatly impact a senior’s quality of life, disrupting their daily routine and preventing them from doing activities they love most. Learn more about the causes, symptoms and treatment options for gout.
Causes of Gout
Gout is caused by too much of uric acid in the blood. The kidneys typically filter out and expel uric acid through urine. However, in some people, the body produces too much uric acid or is unable to get rid of it effectively. This leads to a buildup of uric acid in the blood.
When this happens, the uric acid can form sharp, needlelike crystals in the joints, causing gout. Typically, an attack of gout affects the joint at the base of the big toe, but it can also affect other joints.
Gout Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing gout.
- Age: Gout is more common in people over the age of 60.
- Gender: Men are more likely to develop gout than women because women generally have lower uric acid levels.
- Genetics: Gout has a genetic component and can run in families.
- Diet: Purines are found in foods and break down into uric acid. Consuming foods high in purines can increase the risk of gout.
- Dehydration: Not getting enough water can increase your chances of getting gout.
- Trauma: Trauma or joint damage, like stubbing your toe, can lead to gout. Additionally, your risk of gout is higher if you have had surgery recently.
- Weight: Gout is more common in individuals who are overweight because the kidneys have a harder time filtering out uric acid.
- Medical conditions: Certain health conditions, like high blood pressure, kidney disease, and diabetes, increase your risk of gout.
- Medications: Some medications can increase uric acid levels. These medications include aspirin, beta blockers, and diuretics.
RELATED CONTENT: 5 Low-Impact Exercises for Arthritis
Gout Symptoms
The symptoms of gout in seniors can be sudden and severe. Usually, symptoms come on at night.
- Intense pain: Gout pain may be so severe that even a bed sheet can cause discomfort. During a flareup, pain is likely to be the most severe within the first 12 hours.
- Inflammation and redness: Affected joints may become swollen, tender, and red as a result of the buildup of urate crystals.
- Limited range of motion: Due to the pain, gout can impact your range of motion. Chronic gout can also damage joints, further reducing mobility.
The symptoms of gout typically last for a few days to a week and then gradually subside. However, symptoms may flare up again, and the symptoms of later attacks may be more severe and affect additional joints.
If you or a loved one experiences sudden, intense joint pain, seek help from a medical professional. Additionally, get treatment right away if you have a fever and the affected joint feels hot and inflamed. These could be signs of an infection.
Diagnosing Gout
To diagnose gout, a doctor will perform a physical examination, paying careful attention to the affected joint. They may also request blood tests, x-rays, or other testing. However, gout can only be diagnosed during a flare up, when the levels of uric acid in the body are higher.
Symptoms of gout are closely related to other inflammatory diseases. So it may be best to get a diagnosis from a rheumatologist, a doctor who specializes in arthritis. Seeing the right professionals can help you get the correct diagnosis and the most effective treatment options. Once you have a diagnosis, your primary care physician can help track your symptoms and manage your gout.
Treatment Options for Gout
There is no cure for gout. However, the symptoms can be treated, and the condition can be effectively managed. Treatment for gout in the elderly involves both medication and lifestyle changes. The goals of treatment are to relieve pain and inflammation, prevent future flareups, and reduce the risk of complications.
Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and colchicine are commonly used to treat gout symptoms by relieving pain and inflammation during a gout attack. If you or a loved one experiences chronic gout, a doctor may also prescribe medications to lower uric acid levels in the blood.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes can also help reduce the risk of gout attacks.
- Avoid foods that are high in purines, such as red meat, seafood, and alcohol.
- Drink plenty of water to help flush uric acid out of the body.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on the joints.
- Exercise regularly to improve joint health and reduce the risk of gout.
- Avoid diuretics and other medications that can increase uric acid levels in the blood.
- Incorporate cherry juice, ginger, and turmeric in your diet, which may help naturally manage gout symptoms.
If left untreated, gout can lead to chronic joint pain and damage. It can also increase the risk of other health problems, which is why it's so important for individuals with gout to stick to their treatment plan.
RELATED CONTENT: Natural Ways to Manage Arthritis
Gout Complications
While gout may not seem that serious, it can lead to serious health conditions if not treated properly.
- Tophi: When uric acid levels are too high for too long, uric acid crystals can turn into hard lumps that are visible under the skin. They can form in joints or cartilage. While tophi may not hurt, it can cause joint damage if not addressed.
- Joint damage: Gout causes chronic swelling, which can ultimately lead to permanent joint damage, stiffness, and deformity. To address damage, you might even need surgery.
- Kidney stones: Urate crystals might not just develop in your joints. They can also form in your kidneys, causing kidney stones. These stones can cause severe pain and even damage kidneys, including kidney disease and kidney failure.
- Depression: Chronic pain can lead to emotional and mental challenges, including depression.
How Home Care Helps with Gout Management
Gout is a painful and potentially debilitating condition that commonly affects older adults. When you or a loved one experiences a flareup, call Caring Senior Service. Our caregivers can help you continue your routine and manage daily tasks that may be too difficult due to pain and limited mobility. We can also help you implement a treatment plan to manage your symptoms or prevent future flareups.
Reach out to your local Caring office to learn how we can help.