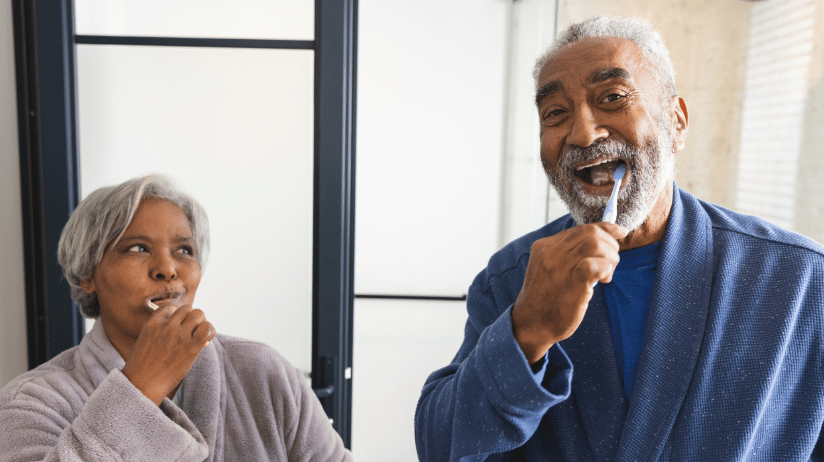
As we age, our mouths and teeth change, which can cause problems if not addressed. Plus, a healthy smile boosts confidence and contributes to overall well-being. So, how does aging affect our mouths? And what can we do to maintain good oral health as we get older?
How Aging Changes Mouth & Teeth
As we age, our bodies undergo various changes. And our mouths are no exception. Here are some of the common changes that occur to the mouth and teeth as we get older.
- Dry mouth: Seniors often experience a decline in saliva production, leading to a dry mouth. Saliva also helps to neutralize acids, wash away food particles, and prevent infections.
- Tooth decay: Decreased saliva can actually lead to increased risk of cavities. As gums recede, this also exposes more of the roots of the teeth, increasing risk of decay and sensitivity.
- Gum changes: Our gums can recede as we get older. Plus, blood supply to the gums can decrease, leading to slower wound healing and an increased risk of gum infections.
- Tooth color: Naturally, enamel wears down over the years, exposing the yellowing tint of teeth underneath. Plus, tobacco, foods, and beverages can stain teeth over time.
- Tooth shape: Our pearly whites may not maintain the same shape throughout our life. Teeth wear down due to chewing or grinding of teeth. Teeth can also become cracked or chipped as we get older.
- Taste: Our taste buds can change too! Medications, dry mouth, and changes in our sense of smell can change our taste buds. This can impact eating habits and nutritional intake.
- Bone loss: Changes in bone density over time can affect the jawbone. As a result, teeth may not be as stable, resulting in tooth loss. Seniors with dentures may need to get a new set if bone density continues to decrease.
Understanding these changes is the first step in developing a good oral health routine for seniors.
Best Practices for Healthy Teeth
Now, let's discover some good oral hygiene practices to keep dental problems at bay and maintain that stellar smile.
Regular Dental Check-Ups
One of the cornerstones of maintaining good oral health is scheduling regular dental check-ups. Seniors should visit their dentist at least twice a year for thorough examinations and professional teeth cleanings. These visits allow for early detection of any potential issues, preventing them from progressing into more serious problems.
As needed, a dentist may recommend additional dental care or more routine dental check-ups to maintain the health of teeth. Listen to your dentist to help prevent oral health problems.
Brushing & Flossing
Daily oral hygiene routines are crucial for everyone, but they become even more critical as we age. Seniors should brush their teeth at least twice a day using a fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush. Flossing is equally important, as it helps remove plaque and debris from between the teeth and along the gumline.
Make sure you don't brush too hard because this can actually damage teeth and gums. Proper technique and consistency are key to maintaining optimal oral health.
Proper Denture Care
For seniors with dentures, proper care is essential. Clean dentures daily using a denture brush and a mild soap or denture cleaner. Remove and rinse dentures after eating to keep them clean. Allow the mouth and gums to rest by taking them out for a few hours each day, like overnight.
Make sure that your dentures fit properly and check in with your dentist for adjustments as needed. Ill-fitting dentures can cause discomfort and oral health issues.
Hydration
Since seniors are more prone to dry mouth, staying hydrated is crucial. Drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day helps stimulate saliva production, which helps protect teeth from decay. Chewing sugar-free gum or sucking on sugar-free candies can also help increase saliva.
Balanced Diet
A well-balanced diet contributes not only to overall health but also to oral health. Seniors should focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and dairy products. These foods provide essential nutrients like calcium and vitamin D, which are key to maintaining strong teeth and bones.
RELATED CONTENT: Understanding the Nutritional Needs of Seniors
Limiting Sugary & Acidic Foods
Seniors should be mindful of their sugar intake, as it can contribute to tooth decay. Additionally, acidic foods and beverages can erode tooth enamel. Moderation is key! If you do consume acidic or sugary foods, rinse your mouth with water afterward and wait at least 30 minutes before brushing.
Tobacco & Alcohol Awareness
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can significantly impact oral health. Tobacco use can lead to a higher risk of gum disease and oral cancers. Seeking support to quit smoking and limiting alcohol intake can contribute to a healthier mouth.
Some types of alcoholic drinks contain sugary mixers, which can lead to tooth decay. Others have high levels of acid that can dissolve enamel. Moderate alcohol consumption to help preserve your teeth.
Fluoride
Fluoride is a mineral that strengthens tooth enamel and helps prevent tooth decay. Seniors should use fluoride toothpaste and, if recommended by their dentist, consider fluoride treatments or mouth rinses.
Maintaining oral health is a lifelong commitment, and as we age, it becomes even more critical. By following these best practices, seniors can ensure that their smiles remain healthy and vibrant throughout their golden years. Remember, a smile is not just a reflection of good oral health but a testament to a fulfilling and joyful life.